Introduction
Pressure control valves are essential components used to regulate and stabilize the pressure in fluid and gas systems across various industries. Without proper pressure control, systems could face operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, or equipment failure. At Regport India Pvt Ltd, a leading manufacturer of pressure control valves, we ensure that our products meet the highest industry standards to guarantee operational safety and reliability. This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of pressure control valves, their types, working principles, and common industrial applications.
What is a Pressure Control Valve?
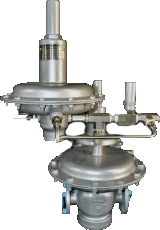
A pressure control valve (PCV) is a device that regulates fluid or gas pressure within a system by controlling the flow of the medium. These valves automatically respond to pressure changes in the system and adjust the flow to maintain stable pressure levels. Pressure control valves are integral to the safe and efficient operation of numerous industrial processes, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and manufacturing.
The main purpose of these valves is to prevent overpressure or underpressure situations that could lead to system failures, equipment damage, or safety hazards.
Types of Pressure Control Valves
Pressure control valves come in different types, each designed for specific applications and pressure management needs. Below are some of the most common types:
- Pressure Reducing Valves
Description: Pressure reducing valves lower the pressure of the fluid or gas from a high-pressure source to a preset, lower pressure level. They are designed to maintain a constant downstream pressure, even if the upstream pressure fluctuates. These valves are often used in systems where the equipment or piping cannot handle high pressure.
Applications:
Steam Systems: Used to reduce steam pressure in heating systems.
Water Supply Networks: Regulates water pressure to prevent overloading of domestic or commercial plumbing.
Compressed Air Systems: Maintains safe and operational pressure levels in air-driven equipment.
- Pressure Relief Valves
Description: Pressure relief valves (PRVs) are safety devices designed to protect equipment from overpressure by releasing excess pressure when it exceeds a preset limit. Once the pressure drops back to safe levels, the valve closes again. PRVs are critical for preventing catastrophic system failures, such as pipe ruptures or equipment explosions.
Applications:
Boilers: Ensures that boilers do not exceed safe pressure limits.
Chemical Plants: Relieves pressure in reactors, tanks, and pipelines during abnormal operating conditions.
Oil and Gas Pipelines: Protects pipelines from overpressure, which could cause leaks or blowouts.
- Back Pressure Valves
Description: Back pressure valves are used to maintain a specific pressure level in the upstream side of the system by restricting flow until the desired backpressure is achieved. These valves are essential in processes where consistent upstream pressure is necessary for optimal system performance.
Applications:
Oil Wells: Controls pressure to ensure stable oil extraction.
Water Treatment Plants: Used in filtration processes to maintain correct pressure for efficient treatment.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Controls pressure during mixing and blending operations in production lines.
- Pilot-Operated Pressure Control Valves
Description: Pilot-operated pressure control valves use a pilot valve to regulate the main valve’s operation. This design allows the main valve to handle higher pressures and flow rates while the pilot valve provides precise control. These valves offer more accurate pressure regulation compared to direct-acting valves and are suitable for systems with varying pressure demands.
Applications:
Gas Transmission Pipelines: Manages pressure in large-scale gas distribution systems.
Hydraulic Systems: Used in hydraulic presses and machinery to maintain stable pressure.
Power Plants: Ensures controlled steam pressure in power generation turbines.
H2: How Pressure Control Valves Work
The working principle of a pressure control valve depends on the type of valve, but the general operation follows a similar pattern:
Sensing the Pressure: The valve detects the pressure in the system through sensors or direct mechanical means.
Comparison to Set Point: The valve compares the detected pressure to a pre-set pressure level. This set point is typically adjustable depending on system requirements.
Adjustment of Flow: If the pressure exceeds or falls below the set point, the valve adjusts the flow of fluid or gas by either opening to relieve pressure or closing to increase it.
Return to Normal Operation: Once the system pressure stabilizes at the desired level, the valve maintains that state until further pressure changes occur.
In systems where precision is crucial, pilot-operated valves or electronic pressure control valves are used for more accurate regulation.
H1: Applications of Pressure Control Valves in Industries
Pressure control valves are used across a wide range of industries, each with specific demands and operational conditions.
- Oil and Gas Industry
Pressure control valves play a vital role in the oil and gas sector, where they manage the pressure in pipelines, wellheads, and processing equipment. High-pressure conditions in these environments could lead to hazardous situations if not properly controlled. For instance, pressure reducing valves regulate gas pressure in transmission lines, ensuring safe delivery to downstream equipment, while pressure relief valves protect critical infrastructure from sudden overpressure.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
In chemical processing facilities, precise pressure control is necessary to maintain the correct operating conditions in reactors, separators, and storage tanks. Pressure control valves ensure the safe handling of hazardous materials, prevent leaks, and protect the equipment from damage due to excessive pressure.
- Power Generation
In power plants, especially those that rely on steam turbines, pressure control valves are critical for maintaining the optimal pressure levels in steam systems. Pilot-operated valves are frequently used in this sector for their ability to handle high pressures and provide precise regulation, ensuring the efficiency of turbines and boilers.
- Water Treatment and Distribution Systems
In water treatment facilities, pressure control valves are used to regulate the flow and pressure of water during filtration, purification, and