Centrifuge /Reactor Blanketing
Centrifuge Blanketing System
The dangers of flash fires and explosions is inherent is many plant operations. Specifically, the combination of volatile solvents and dusts in process vessels, such as a high-speed Industrial Centrifuge, where highly flammable conditions can be created. Unless proper safety measures are undertaken, this situation can potentially lead to catastrophic fires and explosions.
The potential hazards involved in the use of Industrial Centrifuges for the separation of solids from flammable liquids are gaining even greater awareness and importance because of a number of serious incidents involving personal injury or regrettably death. Methods of monitoring and avoiding such hazards are important to all those involved, not just the production operator and safety manager.
- One is the so called timed-volume or continuous-purge approach, in which the vessel is flushed with inert gas initially, followed by a flow of inert gas that assumes that conditions will be maintained below the Minimum Oxygen Concentration level (MOC).
- The second is a pressurised approach, in which the vessel is flushed, and then a positive pressure is maintained within the vessel with the inert gas.
Application
- There is an extensive range of Centrifuge types and sizes. The most common type is the top or bottom discharge filtration batch centrifuge. Other types include the Continuous Decanter Centrifuge, the Disc Stack etc.
- The types of industries using Industrial Centrifuges are similarly diverse. These include the chemical, pharmaceutical, petro-chemical and food industries. Every year a number of explosions involving Centrifuges are reported. Each time the accident enquiry pinpoints human error, equipment failure or bad engineering design as the major causes.
- A typical process cycle of a batch type Centrifuge :
- Centrifuge sweeping or purging with nitrogen gas, usually Nitrogen.
- Feed slurry is introduced to the Centrifuge, i.e. the separation stage.
- Again purge the centrifuge with the inert gas to remove the oxygen level.
- Close Purging operation & start blanketing throughout spinning.
- After final spinning, most of the liquid has been removed from the cake.
- Final remaining solids are discharged from the basket or bowl.
- During all these operations the Centrifuge must be inert either by purging or by blanketing with inert gas.
- The principle behind inertizing is that if one can keep the oxygen level below the minimum oxygen level for combustion (MOC) i.e. 3 – 6% then there is zero probability for an explosion.
Manual Centrifuge Blanketing System.
Semi-Automated / Timer Based System.
Fully Automated / On-Line Oxygen monitoring system.
The System



Brief on the Manual System :

- User-friendly and easy to understand & operate.
- Operator has to operate only two isolation valves.
- Except Nitrogen no other utility required
- No special tools & tackles / expertise are required.
- Minimum corrections to upgrade to Semi or Fully Automated.
- First Stage Reduction: To Reduce From PSA Generation of 2 – 6 Kg/Cm2g to Purging Pressure of 5000 mmWcg
- Purging : Purging the centrifuge system @ Pressure of 5000 mmWcg
- Basket Blanketing : After predetermine purging time (generally 45 seconds for size upto 42” CF), basket blanketing pressure is 150 mmWcg
- Bearing blanketing : To keep the bearing housing portion inert (In case of Provision by manufacturer)
- Proportionate relief : Provided on basket vent to release only excess pressure above 350 mmWcg to & safe guard the basket from over pressurisation.
- Pressure Switches : To make the system further safe, Low Pressure Switch & High Pressure Switch set at 50 mmWcg & 1000 mmWcg respectively are provided alongwith PG for monitoring the basket pressure. In case, if Nitrogen is not coming in from the source, the pressure in the basket drops below 50 mmWcg and PSL operates. In case of contingency with venting, the pressure inside the basket rises to 1000 mmWcg, PSH operates.
First Stage Reduction
- Nitrogen Generation Pressure @ 2 – 6 Kg/Cm2g can’t be exposed to centrifuges as they are designed for lower pressure.
- PSA Generation pressure reduction will be done by (PCV-01 ). This will reduce the N2 source supply pressure to purging pressure of 0.5 Kg/Cm2g.
- In case of failure of regulator, safety relief valve ( SRV-001 ) having a relief set pressure of 1 kg/Cm2g is provided after pressure control valve.
Purging :
- Once material is loaded & lid is closed, switch on the Purging isolation valve, so that nitrogen @ pressure of 5000 mmWcg will rush into the basket ensuring inert atmosphere by displacing, air and in turn oxygen, solvent vapours/ traces through BPRV-A (which set @ of 350 mmWcg).
- Based on the experience purging time can be decided.
- After proper purging switch off the isolate valve & stop the purging.
- In case of timer based system, purging valve will remain open as per pre-set timer & in fully automated system, purging can be hooked up with online Oxygen Analyser.
Basket Blanketing :
- After completing purging and displacing the oxygen through BPRV, “Switch ON” the basket blanketing valve so that Nitrogen @ 150 mmWcg will be fed to centrifuge basket.
- Initially system pressure is 350 mmWcg so N2 won’t enter in the basket, however during centrifuging process once basket pressure drop below 150 mmWcg, N2 will rush into the basket.
- This valve will always monitor the basket pressure and feed the nitrogen based on requirement. In case of non requirement valves goes in close conditions
- This valve should be in “switch on” mode throughout centrifuging.
INDUSTRIES WE SERVE :
PHARMA :
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Back Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019))
- Skid Mounted Pressure Regulating Stations for
- Nitrogen Gas
- Hydrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Anhydrous HCL Gas
- Ammonia Gas
- Carbon Dioxide Gas
- Chlorine Gas
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300 / D950)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Flame arrestors (F100/ F200)
- Breather Valves with built in Flame Arrestors (B900/ B950)
- Manual Centrifuge Blanketing System
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U100)
- Full Automated ie Centrifuge Blanketing System with Online Oxygen Monitoring
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
CHEMICAL :
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Back Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U100/ U200)
- Pump Bypass Valves (Model U100/ U200)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Skid Mounted Pressure Regulating Stations for
- Nitrogen Gas
- Hydrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Anhydrous HCL Gas
- Ammonia Gas
- Carbon Dioxide Gas
- Chlorine Gas
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300 / D950)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Flame arrestors (F100/ F200)
- Breather Valves with built in Flame Arrestors (B900/ B950)
OIL & GAS :
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Pump Bypass Valves (Model U100/ U200)
- Pump Bypass Valves (Model U100/ U200)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019)
- Pilot Operated Relief Valves (Model R020)
- Nitrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300 / D950)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U950)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Flame arrestors (F100/ F200)
- Breather Valves with built in Flame Arrestors (B900/ B950)
STEEL :
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Back Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U100/ U200)
- Pump Bypass Valves (Model U100/ U200))
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019)
- Skid Mounted Pressure Regulating Stations for
- Nitrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300 / D950)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U950)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Flame arrestors (F100/ F200)
- Breather Valves with built in Flame Arrestors (B900/ B950)
POWER PLANT :
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Back Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019)
- Safety Relief Valves – According to Section-I (Model R015)
- Skid Mounted Pressure Regulating Stations for
- Nitrogen Gas
- Hydrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Carbon Dioxide Gas
FOOD & EDIBLE OIL :
- Applications –Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Back Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Safety Relief Valves – Bellow Type (Model R019)
- Skid Mounted Pressure Regulating Stations for
- Nitrogen Gas
- Hydrogen Gas
- LPG
- Natural Gas
- Air
- Carbon Dioxide Gas
- Pressure Regulators (Model D100/ D200)
- Blanketing Regulators (Model D300 / D950)
- Depadding or Blanketing Pressure Relief Regulators (Model U300/ U100)
- Safety Relief Valves – Conventional (Model R012/ R016)
- Safety Relief Valves – Corrosive Service (Model R014)
- Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves or Breather Valves (B100/ B100-P)
- Flame arrestors (F100/ F200)
- Breather Valves with built in Flame Arrestors (B900/ B950)
Centrifuge Blanketing System
- One is the so called timed-volume or continuous-purge approach, in which the vessel is flushed with inert gas initially, followed by a flow of inert gas that assumes that conditions will be maintained below the Minimum Oxygen Concentration level (MOC).
- The second is a pressurised approach, in which the vessel is flushed, and then a positive pressure is maintained within the vessel with the inert gas.
Application
There is an extensive range of Centrifuge types and sizes. The most common type is the top or bottom discharge filtration batch centrifuge. Other types include the Continuous Decanter Centrifuge, the Disc Stack etc.
The types of industries using Industrial Centrifuges are similarly diverse. These include the chemical, pharmaceutical, petro-chemical and food industries. Every year a number of explosions involving Centrifuges are reported. Each time the accident enquiry pinpoints human error, equipment failure or bad engineering design as the major causes.
A typical process cycle of a batch type Centrifuge:
Centrifuge sweeping or purging with nitrogen gas, usually Nitrogen.
Feed slurry is introduced to the Centrifuge, i.e. the separation stage.
Again purge the centrifuge with the inert gas to remove the oxygen level.
Close Purging operation & start blanketing throughout spinning.
After final spinning, most of the liquid has been removed from the cake.
Final remaining solids are discharged from the basket or bowl.
During all these operations the Centrifuge must be inert either by purging or by blanketing with inert gas.
The principle behind inertizing is that if one can keep the oxygen level below the minimum oxygen level for combustion (MOC) i.e. 3 – 6% then there is zero probability for an explosion.
The System
Manual Centrifuge Blanketing System

Semi-Automated / Timer Based System

Fully Automated / On-Line Oxygen monitoring system

Brief on the Manual System
Manual Centrifuge Blanketing System
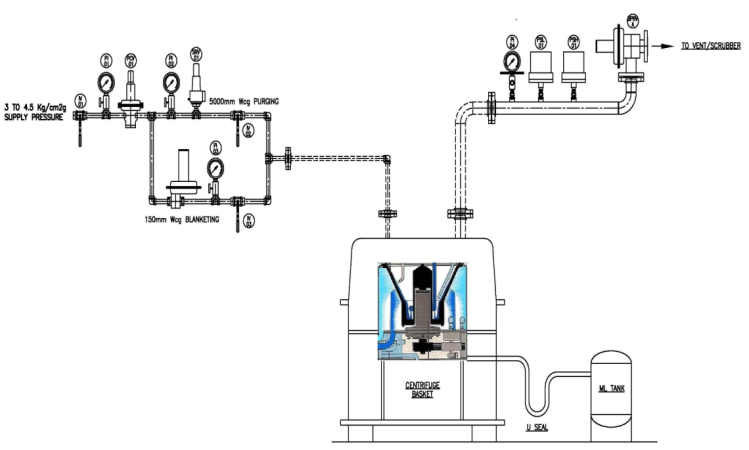
Manual Centrifuge Blanketing System is one of the most preferred system in pharma industry because of the following advantages :
User-friendly and easy to understand & operate.
Operator has to operate only two isolation valves.
Except Nitrogen no other utility required.
No special tools & tackles / expertise are required.
Minimum corrections to upgrade to Semi or Fully Automated.